- The conversion of b-hydroxybutyrate
to acetoacetate occurs by what type of reaction?
oxidation
reduction
dehydration
dehydroxylation
- The active site of an enzyme
is
formed only after addition of a specific substrate.
is
directly involved in binding of allosteric inhibitors.
resides
in a few adjacent amino acid residues in the primary sequence
of the polypeptide chain.
binds
competitive inhibitors.
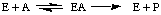
- An enzyme catalyzing the reaction shown above was mixed with
4 mM substrate. The initial rate of product formation was 25%
of Vmax. The Km for the enzyme is
2
mM.
4
mM.
9
mM.
12
mM.
25
mM.
- The velocity (v) of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction
decreases
as the substrate concentration increases.
is
lowest when the enzyme is saturated with substrate.
is
related to the substrate concentration at 0.5Vmax.
is
independent of the pH of the solution.
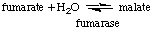
- Fumarase catalyzes the conversion of fumarate to malate.
It has a Km of 5 µM for fumarate and a Vmax
of 50 µmol min-1 mg-1 of protein
when measured in the direction of malate formation. The concentration
of fumarate required to give a velocity of 25 µmol min-1
mg-1 protein is
2
µM.
5
µM.
10
µM.
20
µM.
50
µM.
- The Km for fumarase is approximately 5 µM
for fumarate. The fumarate concentration in mitochondria is approximately
2 mM. If the fumarate concentration dropped to 1 mM, the reaction
rate would
increase
slightly.
decrease
slightly.
decrease
by one half.
stay
exactly the same.
- Hexokinase and glucokinase both catalyze the phosphorylation
of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate. The values of Km
for the enzymes are 10 µM and 0.02 M, respectively. If
blood glucose is 5 mM under fasting conditions and 20 mM after
a high-carbohydrate meal
hexokinase
will function near its Vmax under fasting conditions.
glucokinase
will function near its Vmax under fasting conditions.
hexokinase
will function at less than one-half Vmax after a high-carbohydrate
meal.
glucokinase
will function at less than one-half Vmax after a high-carbohydrate
meal.
- A competitive inhibitor of an enzyme
increases
Km but does not affect Vmax.
decreases
Km but does not affect Vmax.
increases
Vmax but does not affect Km.
decreases
Vmax but does not affect Km.
decreases
both Vmax and Km.
- Enzymes catalyze reactions by
increasing
entropy of a system.
increasing
substrate energy.
altering
reaction equilibria.
lowering
total energy levels of reactants.
decreasing
free energy of activation.
- The functions of many enzymes, membrane transporters and
other proteins can be quickly activated or deactivated by phosphorylation
of specific amino acid residues catalyzed by enzymes called
cyclases.
kinases.
phosphatases.
proteases.
zymogens.