- Which of the following best describes the molecule illustrated
above?
D-glucose
L-glucose
D-fructose
L-fructose

- Which of the following results when the above molecule is
reduced (reduction of the highlighted group)?
glucuronic
acid
galacturonic
acid
glucitol
galactitol
gluconic
acid
galactonic
acid

- Which of the following best describes the molecule above?
a-D-glucofuranose
b-D-glucofuranose
a-D-ribofuranose
b-D-ribofuranose
a-D-glucopyranose
b-D-glucopyranose
a-D-ribopyranose
b-D-ribopyranose
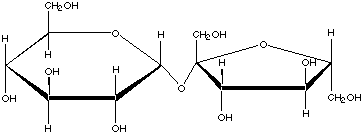
- Which of the following best describes the above molecule?
O-b-D-galactopyranosyl-(1Æ4)-D-glucopyranose
O-a-D-glucopyranosyl-(1Æ2)-D-fructofuranoside
O-a-D-glucopyranosyl-(1Æ2)-D-glucofuranoside
O-b-D-galactopyranosyl-(1Æ4)-D-fructopyranose
- Which of the following does NOT have a reducing end (is NOT
a reducing sugar)?
xylulose
xylose
sucrose
maltose
- Glycoproteins frequently have their carbohydrate portion
attached to the following amino acids EXCEPT
glutamate
serine
threonine
asparagine
- Which of the following are NOT major dietary carbohydrates?
starch
dextrose
lactose
sucrose
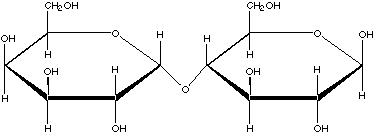
- Which one of the following enzymes will cleave the molecule
illustrated above?
a-amylase
a-dextrinase
lactase
sucrase
a-glucosidase
b-glucosidase
- Which of the following statements concerning glycoproteins
is TRUE?
They
are usually positively charged.
They
never contain branched oligosaccharide chains.
They
contain oligosaccharides that are synthesized on dolichol phosphate
and transferred to serine residues.
They
are degraded by lysosomal enzymes.
They
are all secreted into the blood.
- A patient has a genetic defect that causes intestinal epithelial
cells to produce disaccharidases of much lower activity than
normal. Compared to a normal person, after eating a bowl of milk
and oatmeal, this patient will have higher levels of
maltose,
sucrose, and lactose in the stool.
starch
in the stool.
galactose
and fructose in the blood.
glycogen
in the muscles.
insulin
in the blood.